This could include all indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and salaries of supervisory staff. This allows businesses to capture the full cost of production in their accounting. Let’s assume a company has $32,000 as manufacturing overhead costs and 7,000 as machine hours.
Determine Estimated Manufacturing Overhead Costs

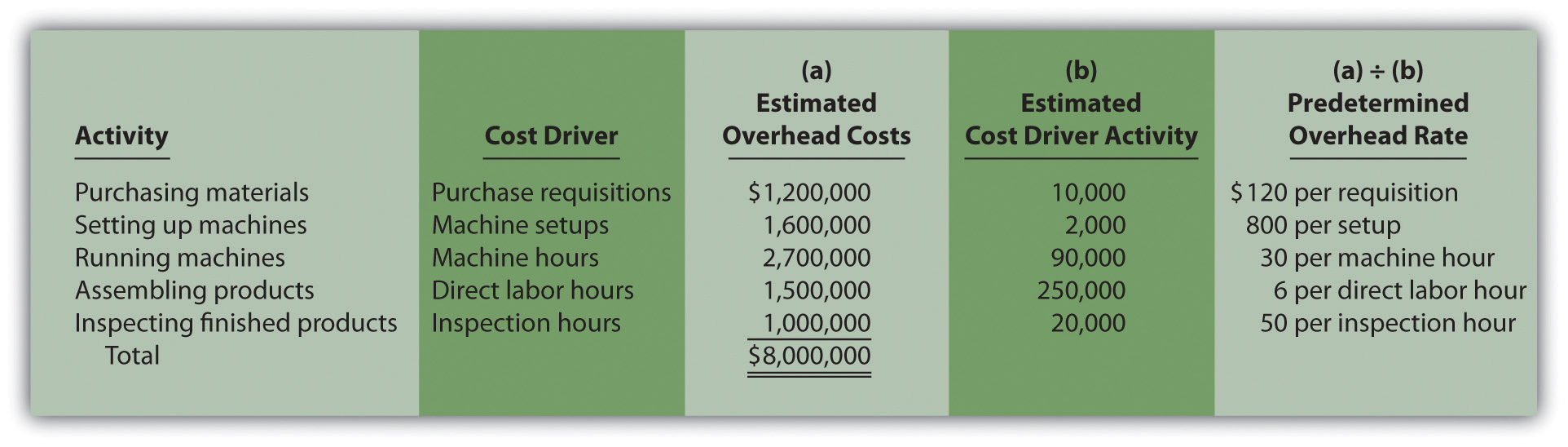
Allocation bases (such as direct labor, direct materials, machine hours, etc.) are used when finding a relationship with total overhead costs. To calculate the predetermined overhead, the company would determine what the allocation base is. The allocation business optimization blueprint base could be direct labor costs, direct labor dollars, or the number of machine-hours. The company would then estimate what the predetermined overhead cost would be and divide them to determine what the manufacturing overhead cost would be.
- As the predetermined overhead rate is an estimate of what the company believes will be the cost for manufacturing the product, the actual costs could be different than what they estimated.
- Let’s understand the steps in calculating the predetermined overhead rate.
- Since we need to calculate the predetermined rate, direct costs are ignored.
- As a result, the overhead costs that will be incurred in the actual production process will differ from this estimate.
Sales and production decisions based on this rate could be faulty
Sourcetable is the optimal tool for anyone looking to enhance their efficiency and accuracy in financial analysis or academic learning. Unlock the power of Sourcetable, an AI-driven spreadsheet that revolutionizes the way you perform calculations. Whether it’s for educational purposes, professional tasks, or personal projects, Sourcetable is equipped to handle any computational challenge with precision and ease.
Estimate budgeted overheads
One of the advantages of predetermined overhead rate is that businesses can use it to help with closing their books more quickly. This is because using this rate allows them to avoid compiling actual overhead costs as part of their closing process. Nonetheless, it is still essential for businesses to reconcile the difference between the actual overhead and the estimated overhead at the end of their fiscal year. Hence, it is essential to use rates that determine how much of the overhead costs are applied to each unit of production output. This is why a predetermined overhead rate is computed to allocate the overhead costs to the production output in order to determine a cost for a product. The predetermined overhead rate is, therefore, usually used for contract bidding, product pricing, and allocation of resources within a company, based on each department’s utilization of resources.
Overhead Rate Formula: A Comprehensive Guide
The more consistency there is between the total overhead and the allocation base, the more accurate the estimate of predetermined overhead will be. The concept of predetermined overhead rate is very important because it is used most of the enterprises as it enables them to estimate the approximate total cost of each job. Larger organizations employ different allocation bases for determining the predetermined overhead rate in each production department.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
With the aid of this rate, companies may set prices on their products or services and ensure their expenses won’t go overboard. Companies should be very careful when using the predetermined overhead rate to make decisions. Company X and Company Y are competing to acquire a massive order as that will make them much recognized in the market, and also, the project is lucrative for both of them. After going to its terms and conditions of the bidding, it stated the bid would be based on the overhead rate percentage.
The choice of allocation base should reflect the principal cause of overhead costs in your operations. For example, assume a company expects its total manufacturing costs to amount to $400,000 in the coming period and the company expects the staff to work a total of 20,000 direct labor hours. In order to calculate the predetermined overhead rate for the coming period, the total manufacturing costs of $400,000 is divided by the estimated 20,000 direct labor hours.
While it may become more complex to have different rates for each department, it is still considered more accurate and helpful because the level of efficiency and precision increases. This calculation acts as a tool for timely reviews of spending, helping to trigger necessary adjustments in expense management in relation to changes in production or sales. We’re a headhunter agency that connects US businesses with elite LATAM professionals who integrate seamlessly as remote team members — aligned to US time zones, cutting overhead by 70%.
If Department B has overhead costs of $30,000 but direct costs of $70,000, then its overhead rate is 43%. Despite having lower total overhead, Department B is less efficient since its overhead rate is higher. This rate would then charge $4 of overhead to production for every direct labor hour worked. It allows overhead to be assigned to production based on activity (DLHs), providing insight into profitability across products. Direct costs are expenses traced to specific products like raw materials or direct labor.
However, this practice does not result in fair allocation of the overheads. So, a more precise practice of overhead absorption has been developed that requires different and relevant bases of apportionment. Businesses normally face fluctuation in product demand due to seasonal variations. Fixed overheads are expected to increase/decrease per unit in line with the seasonal variations. So, the cost of a product in one period may not reflect the cost in another period—for instance, the cost of freezing fish increases in the summer and lowers in the winter. Detailed cost analysis helps to estimate the cost of overheads with accuracy.

